- Home
- /
- News
- /
- Industry News
IEC Standards for electric motors

In 1999, the European Commission established different efficiency classes for electric motors to reduce energy consumption and to create awareness among various industries to the importance of a more sustainable environment.
These efficiency classes were called the EFF standards.
However, in 2008 these EFF standards changed to the current IEC standards for electric motors to overcome the international inconsistencies in regulations between electric motor standards and efficiency classes.
For example, the US established the NEMA standards for electric motors, which differed a lot from the EU standards. These standards were set by a new commission called the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
IE4 motors by Magnetic Innovations
The torque motors designed and manufactured by Magnetic Innovations already fall within the IE4 super premium efficiency class. This can result in enormous energy savings for your operations. Please contact us for more info.
IEC efficiency classes
The following IEC standards were established in 2008:

Since 2014 the power range was extended for electric motors and was set between 0,12 kW and 1000kW. Furthermore, since the 1st of January 2017 electric motors with a rated output of 0,75-375 kW must meet either IE3 efficiency or IE2 if fitted with VSD’s.
International electric motor efficiency standards
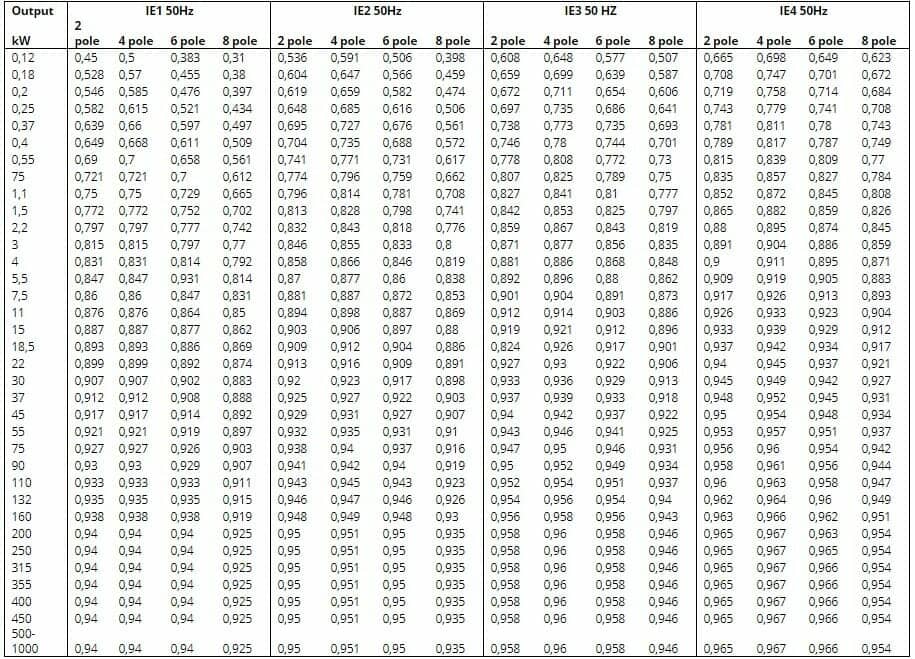
The following table shows a comparison between the in 2008 established IEC standards (IEC/EN 60034-20-01) and other international norms:

Electric motors included by the IEC standards
Single speed electric motors (single and three phase), 50 and 60 Hz
Line-start permanent magnet motors 2, 4, 6 or 8 poles –
Rated output PN from 0.12 kW to 1000 kW
Rated voltage UN above 50 V up to 1 kV
Motors, capable of continuous operation at their rated power with a temperature rise within the specified insulation temperature class
Electric motors excluded by the IEC standards
Motors designed to operate wholly immersed in a liquid
Brake motors, when the brake cannot be dismantled or separately fed.
Single-speed motors with 10 or more poles or multi-speed motors
Motors completely integrated into a machine (for example, pump, fan or compressor) that cannot be tested separately from the machine.
Motors specifically designed to operate:
At altitudes exceeding 4000 meters
Where ambient air temperatures exceed 60°C
In maximum operating temperatures above 400°C.
Where ambient air temperatures are less than –30°C (any motor) or less than 0°C (water-cooled motors)
Where the water coolant temperature at the inlet to a product is less than 0°C or exceeds 32°C
In potentially explosive atmospheres as defined in Directive 94/9/EC
IEC specifications

However, in 2008 these EFF standards changed to the current IEC standards for electric motors to overcome the international inconsistencies in regulations between electric motor standards and efficiency classes.
For example, the US established the NEMA standards for electric motors, which differed a lot from the EU standards. These standards were set by a new commission called the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
IE4 motors by Magnetic Innovations
The torque motors designed and manufactured by Magnetic Innovations already fall within the IE4 super premium efficiency class. This can result in enormous energy savings for your operations. Please contact us for more info.
IEC efficiency classes
The following IEC standards were established in 2008:

Since 2014 the power range was extended for electric motors and was set between 0,12 kW and 1000kW. Furthermore, since the 1st of January 2017 electric motors with a rated output of 0,75-375 kW must meet either IE3 efficiency or IE2 if fitted with VSD’s.
International electric motor efficiency standards
The following table shows a comparison between the in 2008 established IEC standards (IEC/EN 60034-20-01) and other international norms:

Electric motors included by the IEC standards
Single speed electric motors (single and three phase), 50 and 60 Hz
Line-start permanent magnet motors 2, 4, 6 or 8 poles –
Rated output PN from 0.12 kW to 1000 kW
Rated voltage UN above 50 V up to 1 kV
Motors, capable of continuous operation at their rated power with a temperature rise within the specified insulation temperature class
Electric motors excluded by the IEC standards
Motors designed to operate wholly immersed in a liquid
Brake motors, when the brake cannot be dismantled or separately fed.
Single-speed motors with 10 or more poles or multi-speed motors
Motors completely integrated into a machine (for example, pump, fan or compressor) that cannot be tested separately from the machine.
Motors specifically designed to operate:
At altitudes exceeding 4000 meters
Where ambient air temperatures exceed 60°C
In maximum operating temperatures above 400°C.
Where ambient air temperatures are less than –30°C (any motor) or less than 0°C (water-cooled motors)
Where the water coolant temperature at the inlet to a product is less than 0°C or exceeds 32°C
In potentially explosive atmospheres as defined in Directive 94/9/EC
IEC specifications


Key: Vertical 3 Phase ac induction motors, electric motor, Vertical Inverter Duty motor, DC Brake motor Oil Pressure Motor, helical gear motor, AC mini Induction DC gear motor, Gear reducer motor series, NMRV NRV worm reducer series, Worm reducer series, Horizontal Inverter duty, worm gear series, ac motor, vertical gearmotor, helical horizontal gearmotor, gear reduce motor, bevel gearmotor, EFF standards, cyclo gear motor, NMRV gear motor, worm reducer
Newer articles
- Benefits to Using Dolin gear motors (30/04/2019)
- 5 tips prior to designing the gear motors (22/06/2019)
- What are DC Motors Usually Gear Motors (21/06/2019)
- Why use a gearbox with a stepper motor? (13/07/2019)
- Understanding IP Ratings (30/01/2019)
- Coupling Types for Different Applications (01/04/2019)
- How to Select a Gearmotors (01/10/2019)
- What is a DC Motor? (03/06/2019)
- Energy Regulations & Standards (08/12/2018)
- What are Brushless DC Motors (31/05/2019)
Older articles
- The Common Industrial Applications of Worm Gear Motors (30/11/2018)
- Durable Motors and Gear Motors for Industrial Applications (30/11/2018)
- Types of DC Motor (26/11/2018)
- Difference between Stepper Motor and DC Motor (19/11/2018)
- Difference Between Stator & Rotor (19/11/2018)
- Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Induction Motor (10/11/2018)
- Difference Between AC and DC Motor (24/11/2018)
- Three Phase Electric Power Explained (12/11/2018)
- What do IP ratings really mean, and how do they differ from NEMA ratings? (09/11/2018)
- Basic Structure Of Gear Motor Reducer (07/07/2018)





Join